Printed circuit boards are a vital part of fields like electrical, electronics, and computer. Most electronic components emit heat while they are working. The amount of heat varies according to the type of circuit, its working time, device characteristics, etc. Moreover, the electric current flowing through the copper traces produces resistance and as a result, the heat elimination can harm the printed circuit board.
Every printed circuit board has its tolerance against heat dissipation but once the limit is crossed, the heat can harm the PCB and even can result in the melting of PCB. To handle this, there must be proper thermal management steps during the designing process. If you are a designer or want to know about the best practices for thermal management then stay on this article because we have the best practices for you.
What is Thermal Management in PCB?
Thermal management is the way to prevent the PCB from overheating by taking measures to eliminate the heat produced during the working of the PCB. It involves the steps during the designing and working of PCB. This measure also includes the addition of extra components such as fans to eliminate the heat while it is working. These are the crucial steps that are life-saving in multiple cases because the extra head can burn the PCB or even the whole circuit. This may be life-threatening where the circuits are used in bulk amounts.
Why Thermal Management is Important
In PCBs, thermal management enhances the lifetime and performance. It has been seen that the PCBs with the best thermal management had the following advantages:
- Reliability of the working
- Optimized performance
- Energy saving performance
- Avoidance of hotspot areas
- Safety
- Consistent working
- Performance prediction
- Environmental impacts
All these points are valid for almost all types of PCBs no matter at which scale they are working. Moreover, PCs working with a heavy load can not be approved without a proper thermal management system.
Practices for Thermal Management in PCB
The thermal management lasts with the PCB from start to end. It means it is not a single-stage step but it requires planning from start to end. We are highlighting some very basic points that must be kept in mind when dealing with PCBs.
Designing of PCB with Heat Management Measures
The design process is one of the most important steps in this regard. The designers have to consider that thermal management is a crucial part and can not be ignored. The dimensions of the PCB must be vast so that there is more room for heat to dissipate. For small PCBs, the natural heat dissipation mechanism is enough to control the system at an optimized temperature.
When dealing with complex and large PCBS, there is a need for additional components such as cooling fans and heat pipes. Moreover, design the PCB in such a way that the components of the PCB, that dissipate more heat are kept on the edges of the PCB. If there is more than one such component, then these should be placed on the different areas of the PCB. The sensitive components must also be placed far from the heat-dissipating components.
In addition to this, the traces of the copper have to be designed in such a way that the components are placed at a distance. The width of these copper traces is also important in such cases. One must also include what sinks in the design.
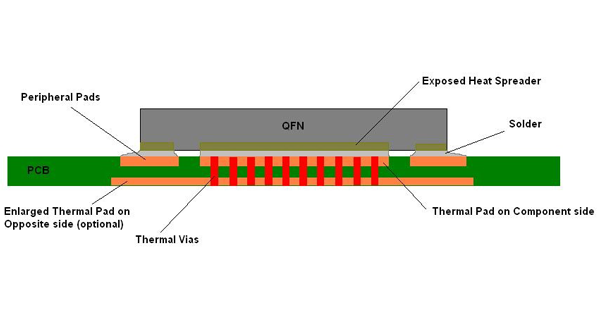
Thermal Pads in PCB
In PCB, the usage of a thermal pad is a great step to avoid the access heat harming the PCB. A good thing about these pads and vias is, they can absorb and bear a lot of heat. So, when placing these pads below the heat-dissipating components of the circuit, the PCB is not affected.
PCB Vias is the thermal transformer that absorbs the heat and then transforms it into the lower layers so that the upper damage may be saved. This can be useful for the circuit that is made with multiple layers and these have a great number of components.
Design of the Traces
In PCBs, the design of copper traces also contributes to the thermal management system. The traces of copper are responsible for the flow of current from one component to the other so that these may work. As I have mentioned before, the width of these traces should be broad. On the other hand, the length of these traces must be short so that the current flowing through them runs smoothly and instantly. In this way, the resistance of the circuit is decreased and less heat is produced.
Natural Convection of Heat Flow
During the design of PCB, the natural convection of the heat must be kept in mind. There must be different ways for the heat to move in the environment. Moreover, do not only rely on natural processes, there must be a plan to force the heat outside the PCB. It is most important in the enclosed systems.
Heat Dissipating Coatings
Thermal management is an important step in the working of PCBs therefore, there are some products that can work well and help the PCB to deal with the heat. In the areas where the chances of heat production are high such as the area where heavily loaded components have to be attached, a coating can help to dissipate the heat.
These are the materials that have chemical properties that can deal with heat well. The coating, in the form of a suspense=sion or liquid, is enough to apply it. The coating then hardens and then the area is ready to deal with the heat.
So, this was all for today related to the PCB. Thermal management is a crucial part of PCB design and work. The companies critically check for the quality of PCB and its ability to bear the heat. These are some general steps that every designer has to take while working on PCB design. We hope it was helpful for you and you have liked it.